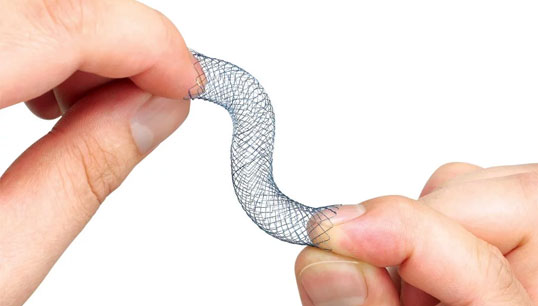
Metal Stents - Biliary
- Non-irritating ends for patient comfort
- Precise compression for target areas
- Maintains length integrity
- Repositioning capability as needed
- Flare ends and partial covering reduce migration risk
- Silicone coating provides protection
- Versatile options, including covered and non-covered versions




